 Running is great for the body and easy to incorporate anytime you choose. The biggest issue is running with this mindset sets up our body to fail. It results in runner’s knee, shin splint, ITB syndrome, stress fractures, and other orthopedic issues that I treat throughout the year. The motto “you have to be fit to run and not run to stay fit” holds true 100% if you want to last long in this individual sport. In a perfect world, without bills to pay and no responsibilities, the motto will be easy to follow. In reality, what should you do? How do I reach my fitness goal and stay away from the doctor’s office?
Running is great for the body and easy to incorporate anytime you choose. The biggest issue is running with this mindset sets up our body to fail. It results in runner’s knee, shin splint, ITB syndrome, stress fractures, and other orthopedic issues that I treat throughout the year. The motto “you have to be fit to run and not run to stay fit” holds true 100% if you want to last long in this individual sport. In a perfect world, without bills to pay and no responsibilities, the motto will be easy to follow. In reality, what should you do? How do I reach my fitness goal and stay away from the doctor’s office?
TAT is the answer to that! Tissue adaptation time or otherwise summarized with the saying “slow and steady will win the race.” The human body is resilient and adaptable when treated with respect and proper care. Our tissues can take a lot of beating, but it has a limit of when to fail. If the time the tissue is being stressed is dragged out over an extended period of time, then the threshold is higher. Basically, the slower the task, the tissue’s capacity (ability to not fail) is greater.
There are two main reasons for tissue failure. This does not equate to pain, but a guarantee to compensate a la “bad (movement) habits.” If the force is fast and our brain cannot tell it to fire fast enough, our muscle and tendon units have a small chance to succeed. If the force is occurring over and over at a small intensity, but the duration of time is short, the tissue will fail. The opposite is true and the reason for stories of people not knowing they have cancer until it reaches the last stage of 4. The body is so adaptable that a slow stimulus, good or bad, will result in “silent” change. This concept is the definition of Tissue Adaptation Time and ONE of the keys to a long-running career.
There is no magic or easy answer to safe running, however, if you blend the two concepts, you will have a powerful upside towards a long and enjoyable running experience. The modern society and footwear design place most people at a disadvantage to not be fit. In order to start running while you are training to get fit, use the concept of starting slow and increasing your mileage at a 10% per 2 weeks is a proven outline for success. It is important to take the emotion out of the training and stop while you are ahead. This is a big reason that you can see varying pain-free running styles; however, if you rely on TAT as your lotto ticket to safe running then you are mistaken. If you incorporate adding options to your running routine, then you are a step closer towards being resilient. Take the time to train on different terrain, speed and directions like backward and sideways.
Tissue Adaptation Time helps you to adapt, but does not build resiliency. Training towards an efficient form will bulletproof your body if your body does take a tumble or suffer an accident. Multiple studies for all body parts, especially for spinal and knee pain, have demonstrated that trauma can shut down and reset your adaptability. Training towards an efficient form will bulletproof your body if your body does take a tumble or accident. Multiple studies for all body parts, especially for spinal and knee pain, have demonstrated that trauma can shut down and reset your adaptability.
Instruction Manual on How to Achieve Running Efficiency
- Running warm-up series (video): All exercise starts with a proper warm-up. An ideal warm-up may take up 20-30 minutes to address our limitations, but this instructional guide is for those who are itching to run today. My warm-up lasts 3-5 minutes and captures all joints and running patterns. Your body will be primed to know what it will be doing and that is the key.
1. Heels, toes, outside and inside ankle walks
2. Marching, heel grab, x-pull
3. Quad pull, butt kick, lunges
4. Tin Soldier, hen peck
5. Hip Swing
6. Skipping (slow, quick, high, lateral, cross)
2. Shock Absorption Test (video): Our front thigh muscle (Quadriceps) is a huge player in absorbing the impact of running. You cannot run properly if you have a muscle of this importance that is shut off. Pain and swelling are two indicators of having a higher chance of a weaker and inhibited muscle. A history of trauma like surgery to the knee is a big reason for a weak Quadriceps muscle. In the video, I demonstrate three tests that you can perform to assess the state of your front thigh muscle. You can apply the three test as an exercise to train for better shock absorption capacity when running.
3. “Healthy” Ankle Test (video): Our ankles and feet are under-managed, but play a huge role in running. Our feet provide sensory information to our brain and body on how it should adapt to the terrain. It is common for people to have a history of ankle sprain or decrease (single leg) balance as they age. A simple test for balance is to stand on one leg and hold this position for 30-seconds with your eyes open. Follow this test by closing your eyes and not sway for 10 seconds. Read my article “To Sprain or Not Sprain (an Ankle)” if you need step by step instructions on how to self-care an old ankle sprain.
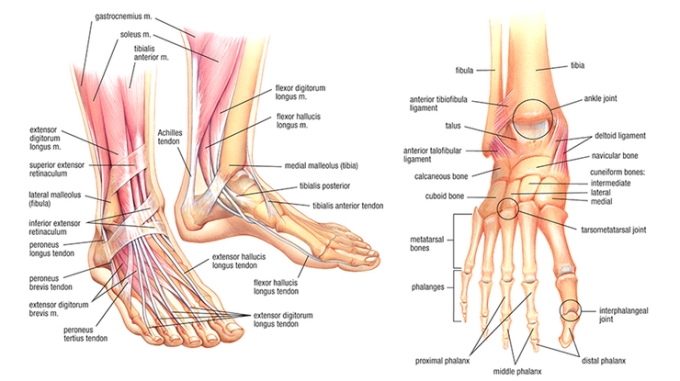
There are two ankle muscles, the Posterior Tibialis and Fibularis Longus muscle, that works together to provide an explosive and low-energy cost movement pattern. Read the article “explosive and low energy cost movement pattern. Read the article “The Secret to Moving Well and Performing like a Professional (Instructions on Foot Care” which explains the role and amazing architecture of our feet. In regards to the two muscles mentioned above, the Posterior Tibialis muscle wraps from the inner shin and expands to all the bones of our arch, including our big toe. This plays a huge role in arch stability. A flat arch posture will result in a weakened Posterior Tibialis muscle. The Fibularis Longus muscle wraps from the outer shin and loops under our feet to connect to our big toe. The Fibularis Longus muscle is a key player when we load our big toe when walking or running. A good analogy of how these two muscles function is where your hands go in opposite direction when twisting a towel from both ends.. The Posterior Tibialis picks up your arch away from the ground. The Fibularis Longus drops your big toe down towards the ground. The explosive movement happens when the towel is released into a whipping motion, releasing the elastic energy that is stored during the twist.
3. Quick Step (video): A big and proven difference between the novice and expert runners is their ability to spend the least amount of time on the ground. There is no right way of landing (rear, mid or fore foot) or style. This concept does not mean that you are on your toes. If you are a rear foot runner, then the time to shift from heel to toe is fast. The video shows how you can train to run like an expert.
Email us at revitalizerehab@gmail.com for three specific strengthening exercises that will support your joints and train your muscles to be elastic and powerful at the same time.
If you need any assistance in running or training for an event, ReVITALize Rehab Club provides FREE 1-on-1 consultation. I hope this article provides a framework for an enjoyable scenic or purposeful running experience. If you add key acupuncture or acupressure stimulation, your running will be taken to a whole new level. ReVITALize Rehab Club blends east meets west rehab and performance care from the inside out! One LOVE and don’t forget to Dream BIG! Move BIG!